Internal IP addresses are only visible to the computers within an internal network. So computers on the internal network can not send data directly to a computer outside of the network. When a computer on the network wants to send data to a computer outside of the network, it sends the data to the gateway. The gateway is the internal IP address of the router. Then the router decides what to do on this data. But NAT (Network Address Translation) will take care of most of the work. There are some programs that NAT was not designed to work with, those are the programs we need to set up port forwarding for.
Port Forwarding simply tells the router which computer on the local area network to send the data to. When you have port forwarding rules set up, your router takes the data off of the external IP address:port number and sends that data to an internal IP address:port number.
1. Open the terminal under windows (Win+R > cmd), and run
ipconfig2. Note down the IP Address of Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection.
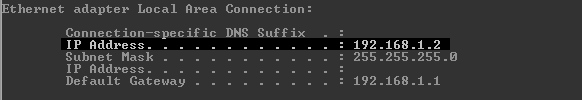
3. Open the browser, go to 192.168.1.1 and login.
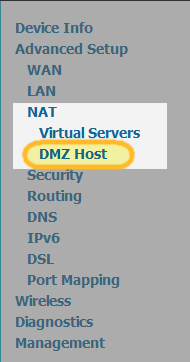
4. Go to Advanced Setup > NAT > DMZ Host. This depends on the type of router. Anyway, there will be a NAT option somewhere.
5. Enter the noted down IP Address from step 2 here.
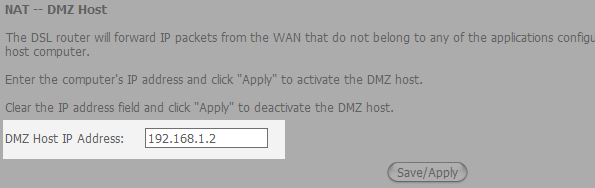
6. Press Save/Apply.